| WPM 고성능 이차전지소재 사업단 소식지 | 2016.12 |
기술정보
다양한 후열처리 온도변수에 따른 Ni-rich 양극활물질의 구조적, 전기화학적 영향에 대한 평가
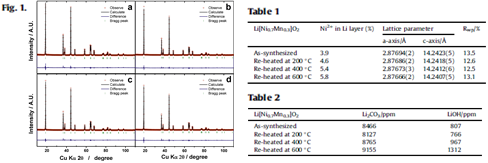 |
| Fig.1. shows Rietveld refinement results of the XRD data for the (a) as-synthesized and re-heated Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2 at (b) 200 ℃, (c) 400 ℃, (d) 600 ℃ in air. It is clear that re-heating of the Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2 at elevated temperatures did not alter the crystal structure without appearance of impurities. Meanwhile, occupation of Ni2+ in Li layers slightly increased with increasing the re-heated temperature; namely, 3.9% for the as-synthesized to 5.8% for the re-heated one at 600 ℃(Table 1). No significant changes were detected in the values for Li2CO3 and LiOH for the as-synthesized and the sample re-heated at 200 ℃(Table 2) |
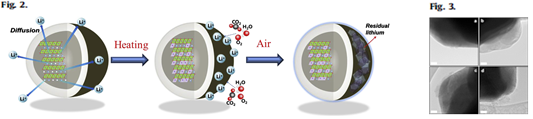 |
| Fig.2 illustrates schematics for the formation of residual lithium compounds. As the lithium diffuses towards surface, vacancies are supposed to be produced in particle inside. Such defects occurred in the particle propelled cationic disorder, so that the occupation of Ni2+ in Li layers further progressed as a result of the re-heating at higher temperature. Fig.3 the formation of lithium residue is also evidenced in the TEM images. Re-heating at (c) 400 ℃ resulted in a clear appearance of foreign material, which is residual lithium compounds, on the surface of Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2, and even the material surface was found to be quite damaged at (d) 600 ℃. |
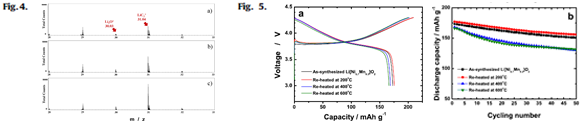 |
| Fig.4 Tof-SIMS data suggest conclusive information on the accumulation of lithium compounds on the surface of Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2 after re-heating. Since the Li2CO3 layer is located on the outermost surface, the resulting intensity of LiC2+ fragments developed significantly as the re-heating temperature elevated up to 600 ℃. Fig.5 (a) The first charge-discharge curves indicate that, although the same charge capacities were observed the re-heated Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2 at 200 ℃ delivered slightly higher discharge capacity, approximately 177 mAh/g, than that of the as-synthesized (173 mAh/g). |
Title : Re-heating effect of Ni-rich cathode material on structure and electrochemical properties(Journal of Power Sources 313 (2016) 1-8) - 세종대학교는 Nich-rich material의 다양한 후열처리 온도에 따른 구조적 영향과 전기화학적 영향을 보고자 Co를 제외하는 가설을 세워 후열처리 과정동안 활물질 내의 Ni2+ 분배 정도를 명확하게 보고자 하였다. - 후열처리 온도가 200 ℃, 400 ℃, 600 ℃로 증가하는 동안 내부의 Li+ 이 활물질 표면으로 이동하게 되고, 구조 내의 결핍된 리튬 층의 자리를 Ni2+가 차지하게 되어 양이온 혼합은 심화된다. 표면에 존재하게 된 Li+은 대기 중에서 Li2CO3, LiOH와 같은 잔존리튬을 형성하게 된다. 이러한 문제점을 해결하고자 세종대학교 연구진은 최적의 후열처리 온도 변수를 적용하여 최적의 조건을 찾고자하였다. - Ni-rich Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2를 공침방법으로 합성하였으며, 500 ℃ 5시간, 900 ℃ 15시간의 열처리 조건을 사용하여 최종물질을 얻었다. 제조된 물질을 200 ℃, 400 ℃, 600 ℃ 후열처리 변수를 설정하여 후열처리 후 물질의 구조적, 전기화학적 특성을 평가하였다. - Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2는 후열처리 온도가 200 ℃ 일 때는 리튬이 내부에서 표면으로 확산이 되지 않음을 cation mixing 정도를 평가하여 확인하였고, 구조내부에 심각한 영향을 미치지 않음을 밝혔다. cation mixing이 감소한 물질은 Li+ 확산이 용이하여 비가역손실이 줄어드는 결과를 얻었다. 후열처리 온도가 증가할수록 구조에 영향을 미치고 내부에서 물질 표면으로 이동한 Li+들이 대기 중에서 반응하여 잔존리튬 함량이 증가함을 확인하였다. |
[성균관대]Porous V2O5/RGO/CNT hierarchical architecture as a cathode material: Emphasis ....
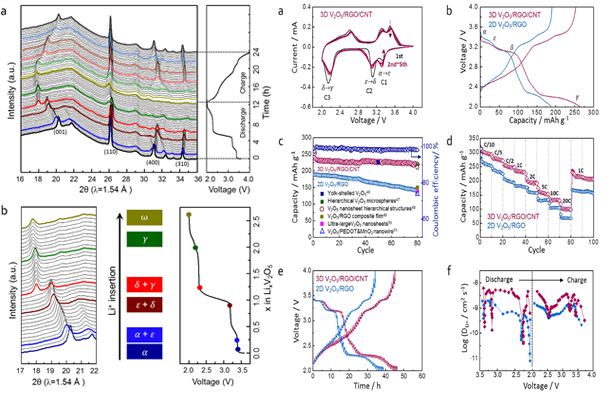 |
| Figure 4. In situ XRD patterns of 3D V2O5/RGO/CNT composite during the first discharge and charge processes in the voltage range of 4.0–2.0 V at 0.1 C Figure 6. Cyclic voltammogram, voltage profiles at 1 C, rate capability, Li+ diffusion coefficients (DLi+) calculated from GITT profile of 3D V2O5/RGO/CNT and 2D V2O5/RGO composites during the electrochemical processes |
| Title: Porous V2O5/RGO/CNT hierarchical architecture as a cathode material: Emphasis on the contribution of surface lithium storage 상용화된 LiCoO2 (140 mAh g−1), LiFePO4 (170 mAh g−1), and LiMn2O4 (148 mAh g−1) 소재에 비해 V2O5/RGO/CNT 양극 물질은 전류속도 1 C에서 80 사이클 이후 220 mAh/g의 용량 및 high C-rate, 20 C에서 100 mAh/g의 상대적으로 높은 용량을 구현. Synchrotron radiation x-ray를 이용한 In situ XRD 및 In situ XANES analysis를 통해 충방전 과정 중의 Li 이온의 탈, 삽입 반응을 실시간으로 관찰, bulk 및 electronic local 구조의 가역성을 확인. Bulk 에서의 Li 이온의 diffusion 반응과 더불어 high surface area를 가진 3D structure의 surface에서의 diffusion 반응이 많은 Li을 저장 하는 데에 기여함을 CV curve의 cathodic peak currents의 정량적 분석을 통해 발견. 기존 Li-intercalated cathode material design에서 벗어나 morphology 변형을 통한 metal oxide/carbon composite의 3D 구조 물질이 고용량 및 고성능 양극 소재의 promising candidate이 될 수 있음을 보여주는 연구. (Scientific Reports, 6:31275)
|
[포항공과대학교]5L-Scale Magnesio Milliing을 통한 SiO2 환원과 음극재로서 활용
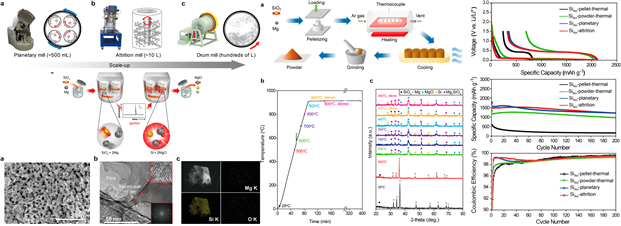 |
- Title: 5L-Scale Magnesio-Milling Reduction of Nanostructured SiO2 for High Capacity Silicon Anodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries - KAIST, 고려대학교와 KIER 연구팀은 쌀의 껍질의 SiO2을 마그네슘과 분쇄과정에서 발생되는 환원 공정을 이용하여 음극재에 사용가능한 Si을 손쉬운 방법으로 합성하였다. - 이는 기존의 유독한 화학반응을 이용한 Bottom up공정 또는 Gas phase를 이용한 Top-down 공정을 대체할 수 있다. 그리고 기존의 마그네슘 열환원 공정보다 간단하게 열처리가 아닌 Milling에서 발생되는 열을 사용하여 합성하였다. - 실험실 규모에서 사용할 수 있는 Planetary miller 뿐만 아니라, Attrition Miller를 통해서도 동일한 수준의 물질을 얻을 수 있었다. - 이전에 사용되던 마그네슘 열환원 공정과 다르게 HF 처리를 거치지 않았기 때문에 SiO2가 소량 잔존하며, 이들이 완충 역할을 하여 수명 특성을 개선할 수 있다. (Nano Letters, 16 (2016), 7261-7269)
|
본 메일은 발신전용입니다. 문의사항은 eunmi.kang@samsung.com으로 문의하십시오.
COPYRIGHT(C) 2013. SAMSUNG SDI INC. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.