2016.07
VOL. 19
NEWS LETTER
기술정보
[포항공과대학교] Micro-Raman Spectroscopy를 이용한 Si의 Stress 변화 분석
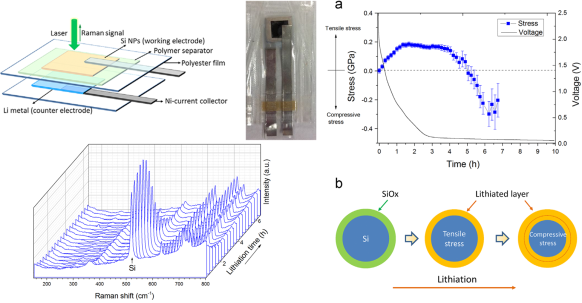 |
- Title: In situ measurement of lithiation-induced stress in silicon nanoparticles using micro-Raman spectroscopy - Stanford uni.의 Yi cui 그룹은 micro-Raman spectroscopy를 이용하여 충방전 과정중 발생되는 Si의 Stress변화를 관찰하여 Nano energy 발표하였다. - Stress변화를 가장 쉽게 확인할 수 있는 Si의 First-order Raman peak을 이용하여, 압력이 증가할수록 Raman shift가 증가하는 것을 관찰하였다. - 이를 토대로 Si nanoparticle은 Lithiation과정에서 초반부에는 내부에 0.2Gpa 수준의 인장응력(Tensile stress)가 형성되며, 일정 이상 Lithiation이 이루어지면 0.3Gpa수준의 압축응력(Compressive stress)가 발생되는 것을 확인하였다. - 이러한 Stress 양상은 Si wafer에서와 다르게 나타나며, Si domain size가 중요한 역할을 하는 것으로 판단하고 있다. (Nano Energy, 22 (2016), 105-110) |
[성균관대학교] Discovering a Dual-Buffer Effect for Lithium Storage: Durable Nanostructured Ordered Mesopo
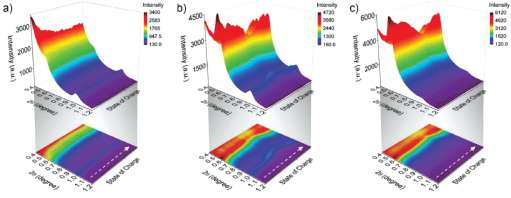 |
| Figure 2. Color-coded 3D contours and projection maps showing small angle X-ray scattering data collected from ordered mesoporous CoxSny electrodes during in operando experiment: a) meso-Co0.5Sn0.5, b) meso-Co0.3Sn0.7, and c) meso-Co0.1Sn0.9 |
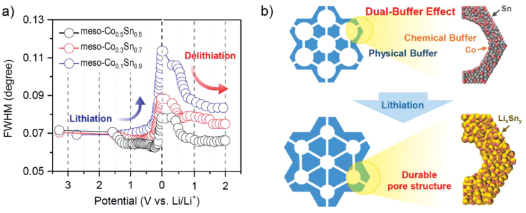 |
| Figure 4. a) The plots of the FWHM with respect to the potential during the lithiation -delithiation process. FWHM value is estimated from the scattering peak fitting with a Lorentzian function. b) Schematic illustration of the buffer effects for the inactive element incorporation and mesostructure, and ex situ TEM images of fully delithiated. |
- Title: Discovering a Dual-Buffer Effect for Lithium Storage: Durable Nanostructured Ordered Mesoporous Co–Sn Intermetallic Electrodes - 리튬 이차전지용 주석계 합금 나노 전극 소재를 개발해 전지의 수명 저하 현상을 해결. - 나노 소재 합성기술을 이용, 두께가 5nm (머리카락의 1만분의1) 에 불과한 주석과 코발트의 합금을 규칙적인 벌집 형태로 배열해 전지 수명이 급격하게 저하되는 문제를 해결할 수 있는 기반을 마련. - 특히 충·방전이 될 때 리튬 이온전지 내부에서 발생하는 전극 소재의 부피 변화를 방사광가속기를 이용해 실시간으로 관측함. - 주석 기반의 벌집 형태 Intermetallic mesoporous CoxSny 나노 물질을 합성하여 전극의 부피 변화를 감소시킴으로써 차세대 리튬이온전지를 설계함에 있어 새로운 방법 및 계기 제시. (Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2800–2808) |
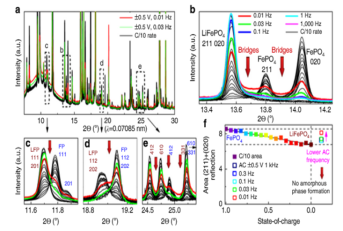
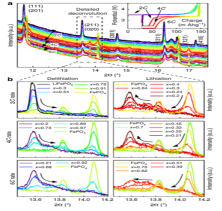
[서울대학교] In-operando XRD-EIS를 통한 LiFePO4의 고용체반응 관찰
|
||||
- Title: Combined operando X-ray diffraction-electrochemical impedance spectroscopy detecting solid solution reactions of LiFePO4 in batteries - Switzerland의 Paul Scherrer Institute에 Petr Novak 그룹은 XRD와 EIS를 결합하여 In-opeando 방식으로 Li-ion battery의 양극 소재인 LiFePO4 (LFP) 의 solid solution reaction을 확인하였다고 Nature Communications에 발표하였다. - In-operando XRD-EIS란 짧은 시간 내에 소재의 XRD data를 얻는 중에 EIS 방식을 통해서 충전과 방전의 cycle을 빠르게 반복하는 것을 말한다. 이러한 방식을 통해 매우 빠른 충전과 방전을 거듭하는 중에 소재가 어떻게 상변화하는지 확인할 수 있다. 특히 빠른 rate에서는 kinetic적인 properties를 확인할 수 있어 최근 주목받는 기술이다. - LiFePO4 양극소재는 최근 중국에서 안정적인 전기자동차용 양극소재로 많이 이용하게 되면서 주목받고 있는 물질이다. 이 물질은 다른 양극소재와는 다르게 충전과 방전 중에 two phase reactions를 하는 물질로 알려져 있다. 하지만 이는 kinetic적 요소를 고려하지 않은 thermodynamic적 상변태도에 따른 현상이며 kinetic적 요소를 충전과 방전 속도를 높임으로서 추가적으로 확인할 수 있다. LiFePO4를 높은 속도로 충전과 방전을 하였을 때, LFP의 peak과 FP의 peak 사이에 ‘Intensity bridges’가 올라오는 것을 통해 two phase reactions가 아닌 intermediate phases를 만드는 solid solution 반응을 하는 것을 확인하였다. (Nature Communications , 2015) |
본 메일은 발신전용입니다. 문의사항은 eunmi.kang@samsung.com으로 문의하십시오.
COPYRIGHT(C) 2013. SAMSUNG SDI INC. ALL RIGHT RESERVED.